For KNX cables,
low attenuation counts
(...and is measured)
For KNX cables,
low attenuation counts
(...and is measured)
Part 1
What is cable attenuation?
Attenuation is one of the most important characteristics of communications and control cables. It is the loss of signal when running through the cable. It is expressed in dB per cable length, e.g. dB/100m. Of course, the lower the attenuation, the better the cable.
How is cable attenuation measured?
Cable Attenuation is measured with vector network analyzers, such as those shown in the photo below. As we are usually measuring attenuation over a range of frequencies, best representation is with a XY chart, with frequency on the X-axis and attenuation on the Y-axis
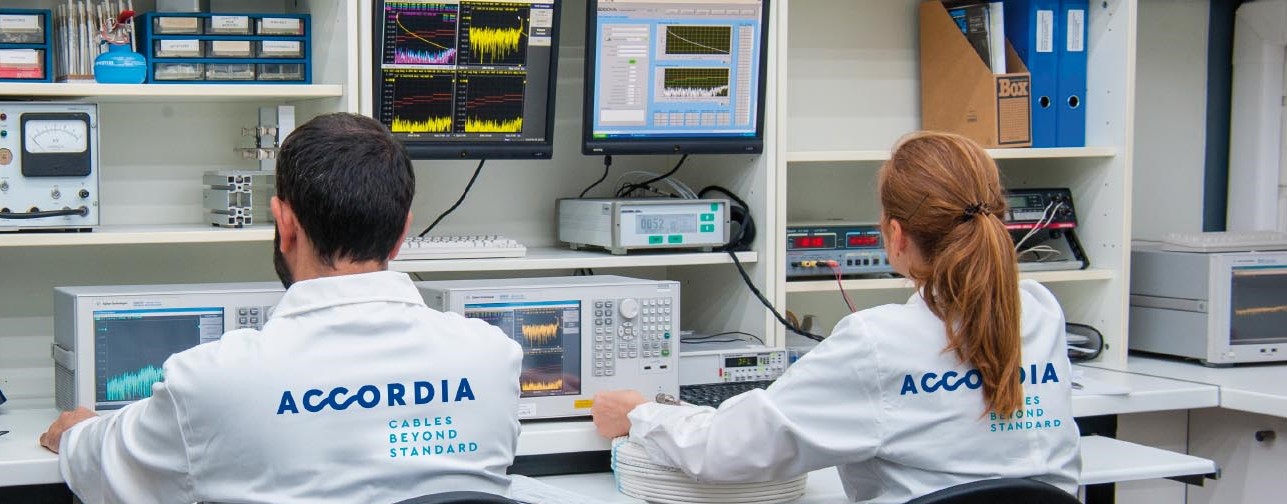

What attenuation must a cable used in KNX installations have?
According to KNX Specification, Volume 09.01, maximum attenuation of TP1 KNX cable is as follows:
Frequency ≤ 50 kHz, maximum 15 dB/km
Frequency 50-500 kHz, maximum 15-35 dB/km
Frequency 0,5-5 MHz, maximum 35-95 dB/km
Frequency 5-25 MHz, maximum 95-200 dB/km
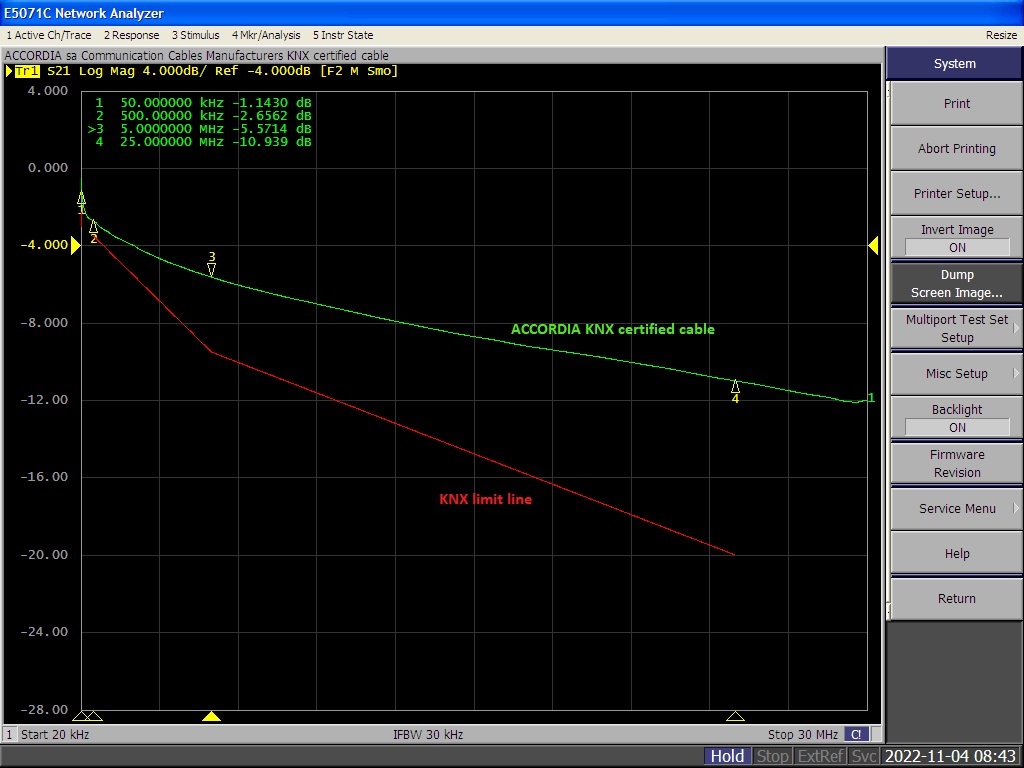
Can you show us an attenuation measurement of a KNX cable?
The image below is a screenshot from an actual attenuation measurement. The red line represents the KNX specification limits. Above the red line is a Pass, below is a Fail. The green line is an actual measured attenuation curve of Accordia KNX certified cable. Not only it's a pass, it goes way beyond the limits.
Do all BUS or KNX cables have the same attenuation?
Absolutely not.
Attenuation depends on many parameters, like the diameter and conductivity of the wires, the material and dimensions of the insulation, the twist pitch, but also on the precision of the production process of each manufacturer.
More on this will follow in the second part.
...to be continued
Ιncrease font size
Α- / Α+
Underline links
Increase contrast





